The James Webb Telescope has discovered the existence of an ancient galaxy larger than our own Milky Way, which threatens to turn cosmology upside down.
According to astronomers, the first galaxies formed around dark matter Live sciences. However, a newly discovered galaxy appeared approximately 13 billion years before this process occurred.
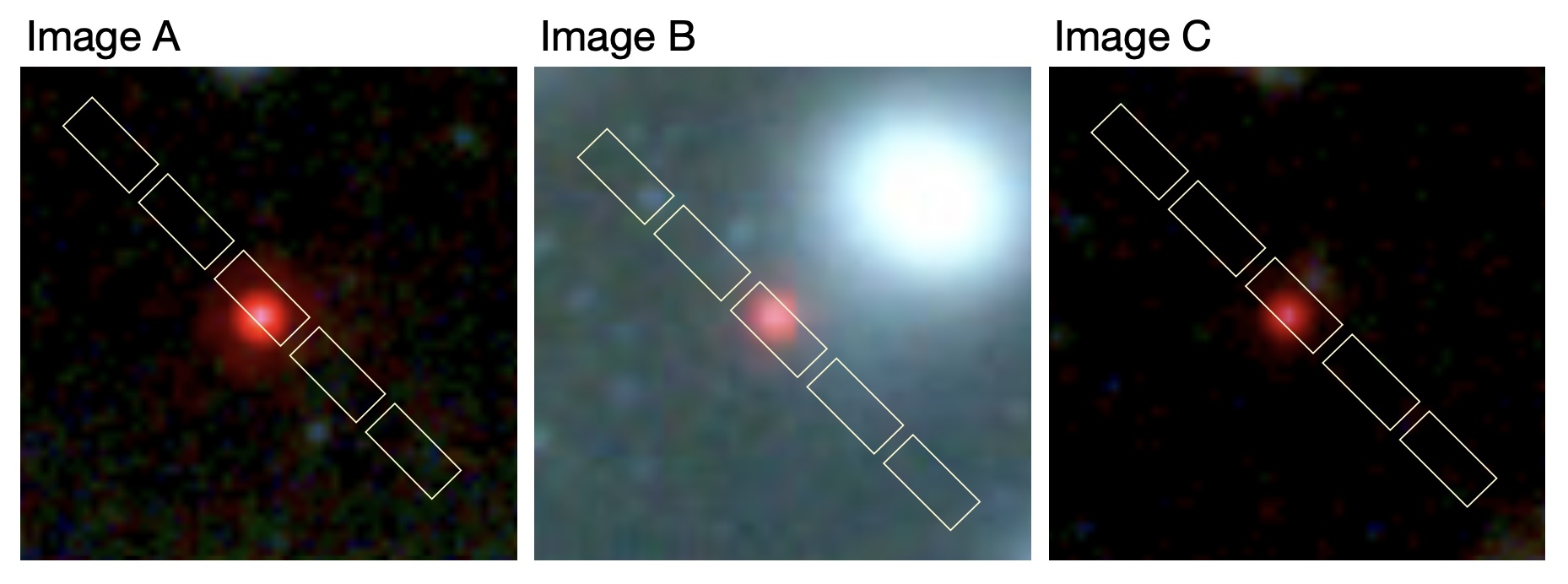
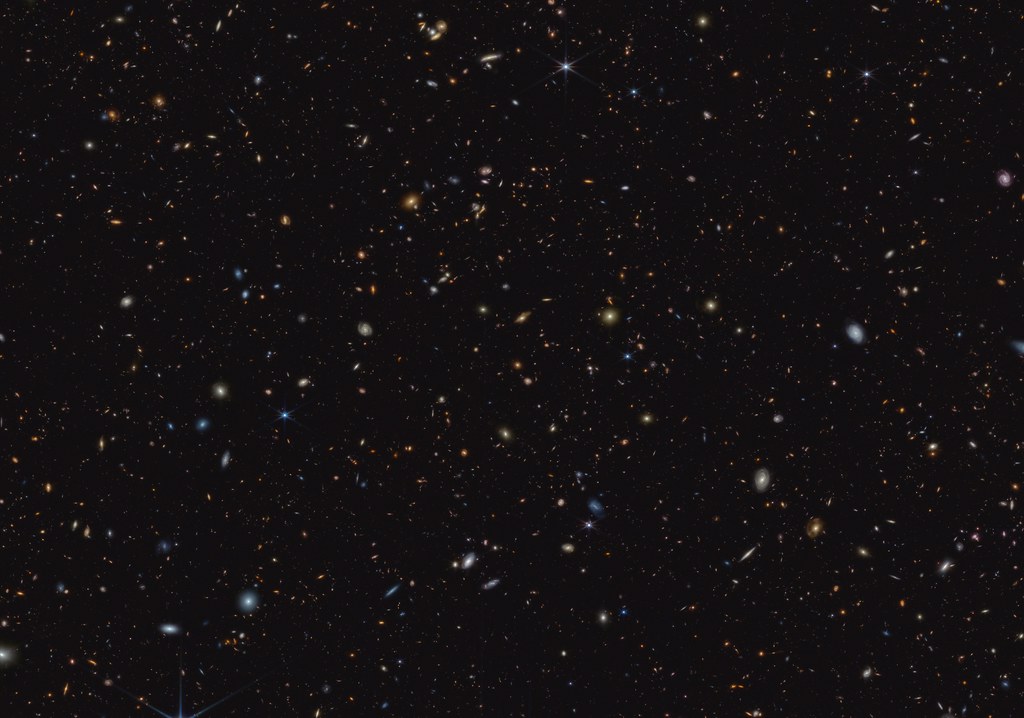
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has discovered a galaxy in the early universe so massive that it shouldn't exist. According to the study's authors, this poses a major challenge to the standard model of cosmology.
The galaxy, called ZF-UDS-7329, contains more stars than the Milky Way. This in itself is not exceptional. But this galaxy formed during only the first 800 million years of the universe's 13.8 billion year lifespan. This means that dark matter did not fuel their formation, contrary to what the standard model of galaxy formation suggests.
How this could happen is not clear. But the James Webb Space Telescope has previously discovered other inexplicably massive galaxies in the early universe.
Maybe the current model is not correct at all?
“Extremely massive galaxies at this early stage of the universe pose major challenges to the standard model of cosmology,” study co-author Claudia Lagos, a professor of astronomy at the International Center for Radio Astronomy Research, said in a statement. Massive dark matter structures, which are, in theory, the necessary ingredients to hold early galaxies together, would not have had enough time to form at such an early stage in the universe.
Light travels at a certain speed in the vacuum of space, so the deeper we look into the universe, the more light we capture, and the further back in time we go. This allowed researchers to use the James Webb Space Telescope to discover ZF-UDS-7329, which dates back approximately 11.5 billion years. By examining the spectrum of incoming light, they found that the emitting stars were born about 13 billion years ago.
How did the universe evolve today?
Astronomers don't know for sure when the first star balls began forming the galaxies we see today. According to their previous estimates, the process began slowly, in the first few hundred million years after the Big Bang.
According to current theories, dark matter halos merged with gas to form the first germs of galaxies. After the first 1-2 billion years of the universe, protogalaxies entered adolescence and transformed into dwarf galaxies. Then they started devouring each other to grow into galaxies like ours.
However, the discovery of the new ancient galaxy refuted this view.
Not only did the galaxy crystallize without accumulating enough dark matter to grow it, but it suddenly entered a quiescent state shortly after forming stars. Star formation stops.
“This pushes the boundaries of our current understanding of galaxy formation and evolution,” said Themia Nanayakkara, co-author of the study and an astronomer at Swinburne University of Technology in Australia, in a statement. “The key question now is how these stars form so quickly so early in the universe, and what are the mysterious mechanisms by which they suddenly stop star formation when the rest of the universe goes on.”
The next steps for researchers include searching for more of these galaxies. If they find one, it could seriously contradict previous ideas about galaxy formation.
Worth reading: