Analysis of samples taken from the asteroid Ryugu allows us to conclude that the jet has wet melting.
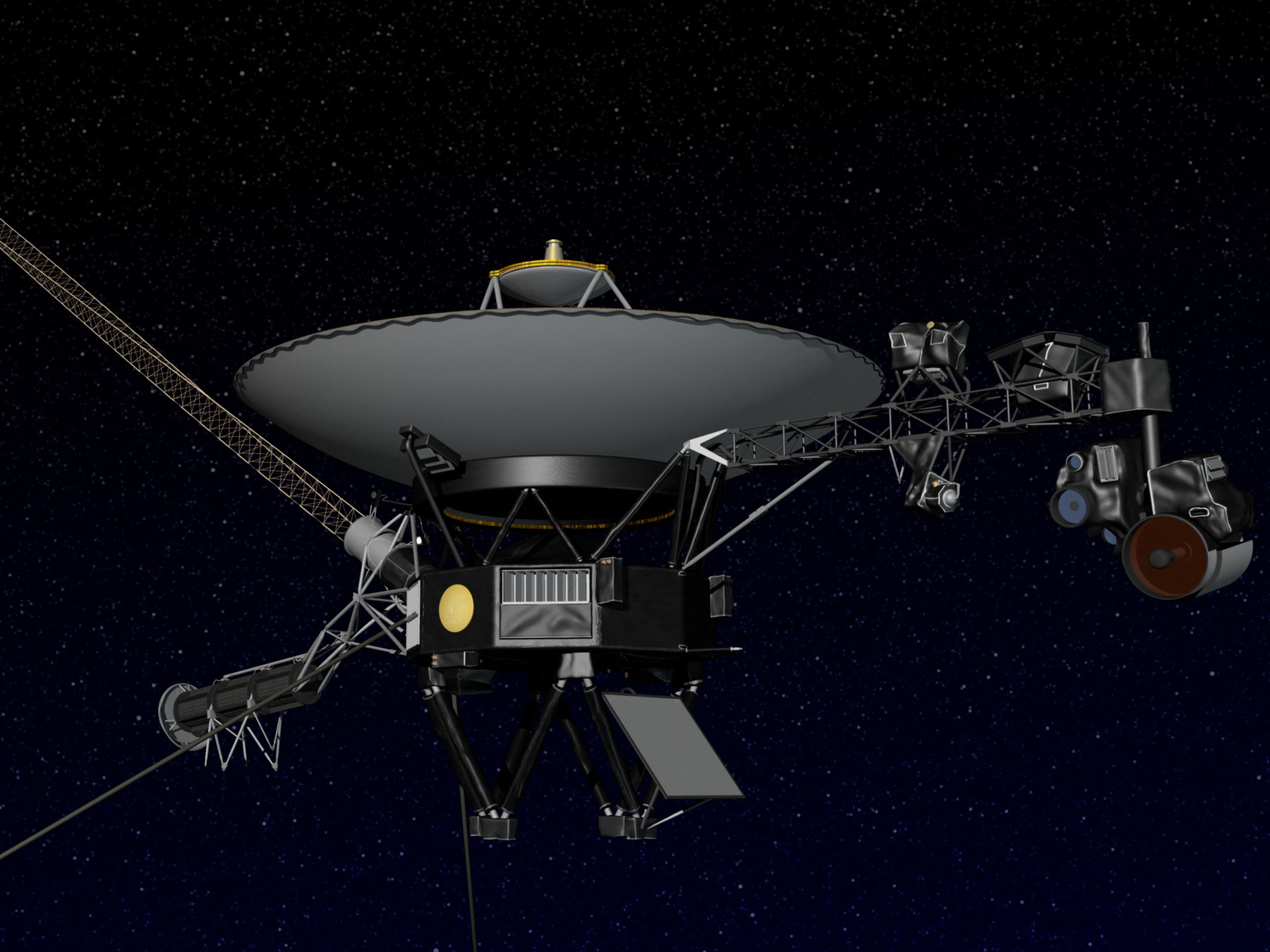
Three years ago, the Japanese probe Hayabusa-2 returned with a sample of material weighing about 5 grams collected from asteroid 162173 Ryugu. By examining the grains, researchers can look into the state of the solar system, because unlike meteorites, the grains brought to Earth were not contaminated as they passed through the Earth's surface. The results of their tests are included in the report Advancement of science In a magazine published.
Hayabusa-2 probe near asteroid Ryugu. (Vansia drawing:JAXA/ISAS)
It has already been discovered during previous examinations that Ryugu actually belongs to the carbonaceous chondrites, that is, to the group of asteroids whose material is rich in carbon, volatile substances (including copper) and organic materials. Although the distribution of material in carbonaceous chondrites is generally similar, the amount of crust has been observed to differ from what is usual in typical cases. The element's concentration moves between much wider boundaries on Ryugu's surface than on other asteroids.
Samples of signals A0107 and C0108 were analyzed during the assay. (Conservative Party:jaxa)
The explanation of the phenomenon is of interest to the research conducted on Karam records 54 and 52 (54Commercial Record, 52Cr) focused their efforts. The mass of the ice sheet could provide a clue to explore the asteroid's past, since crustal compounds are soluble in water, so in the past, hydrochemical processes affected the crust's distribution. Later, during the dry period of the Ryugu event, gold stabilized, remaining unchanged for the rest of the year. The distribution of the element thus preserved traces of the past aquatic environment.
The two secret books were examined in a similar manner (50You and 47Ti) as well as gold, and they observed that while the color of the titanium isotopes barely differed in individual samples, the color of the cremizo isotopes showed a color difference of about twice as much. The results supported the hypothesis that Ryugu's history is similar to that of other carbonaceous chondrites.
The direction of the cream probably occurred in millimeter steps on the surface of Ryugu. The flow of water in thin veins in the middle of the pores caused differences in the distribution of clay over millimeter distances, after the deposit of secondary layers marked with carbon. (Conservative Party:University of Tokyo/JAXA)
Coal chondrites are difficult to study on Earth's surface, because they are rarely found on Earth's surface. That is why it was important that the sample of material obtained from Ryugu was delivered to Earth in its original state in the Hayabusa capsule. Carbonaceous chondrites are among the most water-rich asteroids, and it cannot be ruled out that this asteroid contributes to delivering water to the Earth's surface in large quantities.
From the distribution of crusts, we infer that water probably interacted with the crust in the first few million years of the body's (and solar system's) formation. It is possible that the basic chemical processes of water occurred when Ryugu was part of a larger body. After this body of water was torn into six parts by the impact, water erupted from pieces of debris. Some of the water can leave immediately after impact, while the rest can leave gradually and slowly. Today, the mound known as Ryugu is completely dry, at least from the outside it looks that way.
NASA and JAXA research teams are examining samples collected from the asteroids Ryugu and Bennu by space probes. In the photo you can see the air tank in which part of the Hayabusa-2 prototype was sent to NASA's Johnson Research Center for testing. (Conservative Party(NASA/Robert Markowitz)
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) is also making samples from Riogor available to specialists applying for research duties for further examination. The teams selected for this year's competition will be determined during December, and successful contestants will be awarded their samples in January. The next research call will likely be published in July 2024.
Meanwhile, the Hayabusa-2 probe continues its mission under the name “Hayabusa Sharp”, and in 2026 and 2031, respectively, it will launch a 2001 cc21 and 1998 KY26 You will fly through asteroids.
Link articles:
Ryugu material
Origin of Ryugu
The most amazing materials
Quickly: Santa Claus's package has arrived
Link links:
Ryugu: Water Mist (Sky and Telescope)
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's research answers the analysis of samples collected by Ryugun