In 2011, the European Space Agency (ESA) approved Project Euclid with a budget of €1.4 billion aimed at dark energy research. During the six-year mission, the researchers want to survey a previously unimaginable number of galaxies, a total of 1 billion, using the space telescope.
MTI has announced that the survey will cover a third of the sky, and will look back in time at galaxies whose light began when the universe was a quarter of today’s age of just 13.8 billion years — Joseph Kovacs, Gotthard Astrophysical Observatory ELTE can read in an astronomical article.
Although the task is monumental, Euclid’s primary goal is surprisingly simple. Based on the data you collect, I want to determine the value of a single number marked w
– wrote the astronomer, referring to the article in the journal Science. He added that wa describes the effect of dark energy. This mysterious anti-gravity force is attributed to the acceleration of the expansion of the universe.
All measurements so far indicate that the value of aw is close to -1. If it turns out to be exactly -1, it would confirm the “trivial” solution to the nature of dark energy, namely that it is nothing more than a simple adjustment made by Albert Einstein in his theory of gravity, called the cosmological constant , which lends empty space the kind of innate flexibility it gives,” the astronomer wrote, adding that such a solution would be the worst possible outcome for cosmologists, because they would only get a useless factor that says nothing about where dark energy comes from or why it is so valuable.
If it deviates even slightly from -1, or better, its value changes over time, it could lead cosmologists in the direction of a comprehensive new theory, from which new physical insights could emerge.
József Kovacs added it.
The European Space Telescope is much more efficient than its predecessors
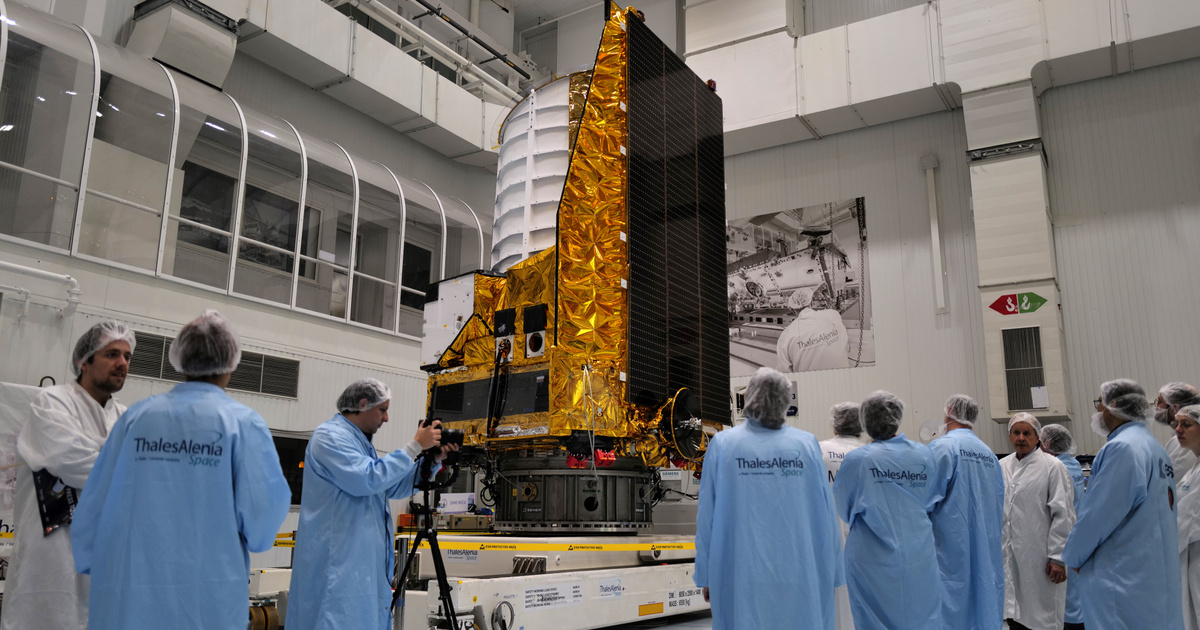
The space telescope is currently in a “clean room” in Florida awaiting launch and the subsequent month-long trip to the L2 gravitational equilibrium point 1.5 million kilometers from Earth, where the James Webb Space Telescope also operates. After reaching L2 and a few months of calibration, Euclid will begin scanning 36 percent of the sky.
In just two days, it will survey as much of the sky as the Hubble Space Telescope has done for more than three decades.
The astronomer explained that it will capture an estimated 10 billion galaxies, stars and objects in the solar system, and outlines the goals of the new study for the James Webb Space Telescope and large ground-based telescopes.
From the tsunami data, the Euclid Union analyzes images of a billion galaxies from a lensing point of view, as well as spectral images of tens of millions of galaxies to determine their spatial position – read Joseph Kovacs’ article.